Unraveling the Potential of Thermoelectric Materials in Electronics
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the search for efficient, renewable energy sources remains pivotal. Amidst this quest, the spotlight is currently on an underdog: Thermoelectric Materials. These are unique substances capable of converting waste heat into usable electricity, which could revolutionize the way we power our electronics.
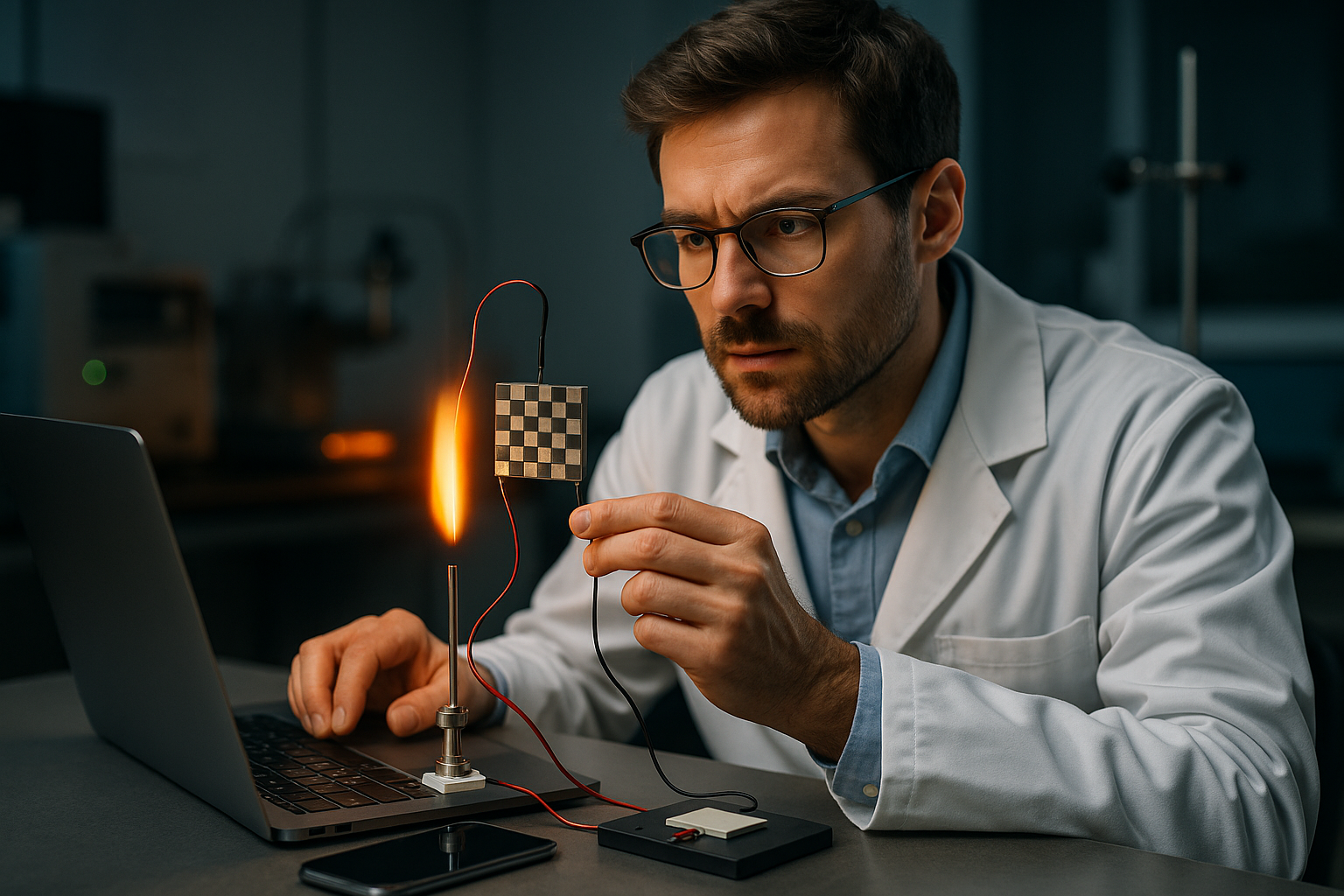

A Background on Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials are not new to the scientific community. They were discovered in the early 19th century by Thomas Johann Seebeck, who observed that a temperature difference across certain materials could generate an electric current. This phenomenon, known as the Seebeck effect, laid the foundation for thermoelectric technology.
Historically, these materials have been used in niche applications—like powering spacecraft during the Cold War era. However, with the escalating need for renewable energy sources and efficient power management in electronics, thermoelectric materials are receiving renewed attention.
The Present Scenario: Thermoelectric Materials Making Headlines
Recently, the tech world has been abuzz with news of advancements in thermoelectric materials. Researchers across the globe are tirelessly working to enhance the efficiency of these materials, making them viable for widespread use.
A team of scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, for instance, has developed a new thermoelectric material composed of common elements like oxygen and copper. This material has demonstrated promising efficiency in lab tests, igniting hope for a sustainable, cost-effective solution to power electronics.
The Market Impact and Price Point
The potential market impact of thermoelectric materials is enormous. They could revolutionize the way we power our electronics, from smartphones to laptops, potentially reducing our reliance on traditional, non-renewable energy sources.
As for the price point, it’s too early to provide an accurate estimate. The cost will depend on various factors, including the efficiency of the material, the scale of production, and market demand. However, with ongoing research and the promise of mass-production, thermoelectric materials could become an affordable solution in the long run.
The Future of Thermoelectric Materials in Tech
The future of thermoelectric materials in electronics looks bright. They could enable us to harness the waste heat generated by our devices and convert it into usable electricity. This not only makes our devices more energy-efficient but also reduces their carbon footprint.
Moreover, the use of thermoelectric materials could extend beyond electronics. They could be used in industries that produce a significant amount of waste heat, such as steel and power plants, and even in our homes—imagine your refrigerator powering itself!
Wrapping Up
Thermoelectric materials are stepping out of the shadows and into the limelight, promising a sustainable, efficient way to power our electronics. The ongoing advancements in this field are a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation in the tech world. While there is a long road ahead, the potential of these materials is undeniable. They could be the game-changer we’ve been waiting for in our quest for renewable energy solutions.